When it comes to the CHMOD (change mode) command, there are three major permissions The CHMOD (change mode) groups are you, the owner, the UNIX group and anyone else A common CHMOD (change mode) command would look something like, "CHMOD 755" This command will let you rename, remove or add a file in addition to reading or editing a fileYou can access it through the path \\wsl$ on Windows Using the Ubuntu file system might create other issues But file permissions wont be one because you would solely use the Ubuntu file system and sync these files to Windows (not the other way around)Type chmod 755 foldername, and then press Return This changes the permissions of the folder to rwxrxrx When it comes to using the ls and chmod commands, practice makes perfect Try modifying the permissions on a couple of sample files Chmod x
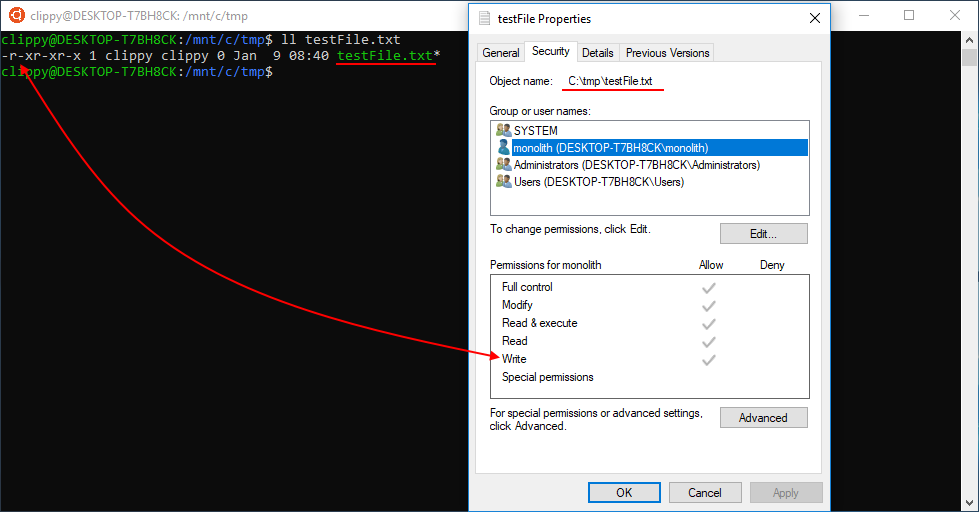
Chmod Chown Wsl Improvements Windows Command Line






